Overview
 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Causes
Morton's neuroma seems to occur in response to irritation, pressure or injury to one of the nerves that lead to your toes. Factors that appear to contribute to Morton's neuroma include. High heels. Wearing high-heeled shoes or shoes that are tight or ill fitting can place extra pressure on your toes and the ball of your foot. Certain sports. Participating in high-impact athletic activities such as jogging or running may subject your feet to repetitive trauma. Sports that feature tight shoes, such as snow skiing or rock climbing, can put pressure on your toes. Foot deformities. People who have bunions, hammertoes, high arches or flatfeet are at higher risk of developing Morton's neuroma.
Symptoms
A Morton's neuroma causes a "burning" sharp pain and numbness on the bottom of the foot in the involved area, and this pain and numbness can radiate to the nearby toes. The pain is usually increased by walking or when the ball of the foot is squeezed together and decreased with massaging. It may force a person to stop walking or to limp from the pain.
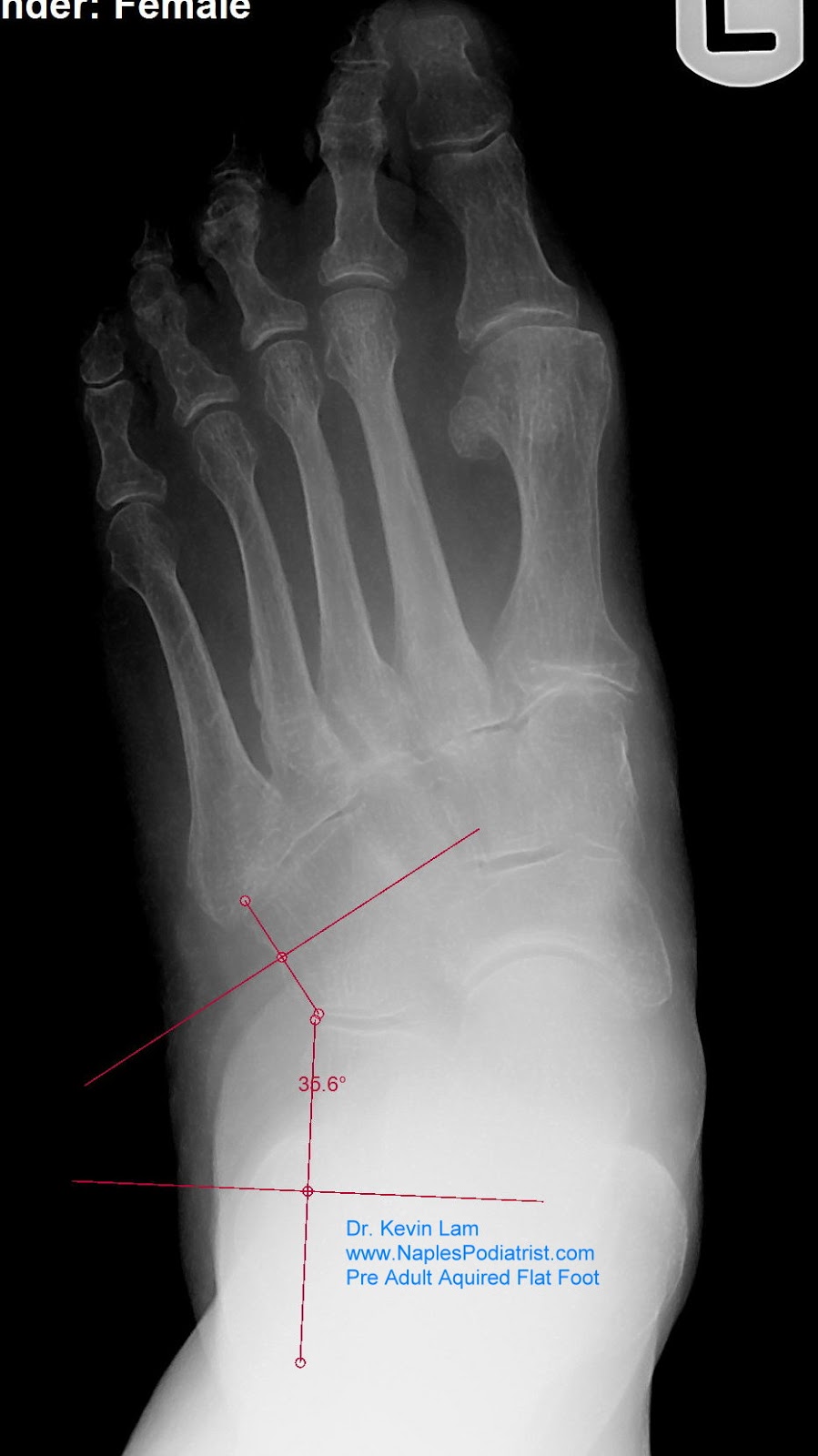
Diagnosis
You might first seek advice from your family doctor about your foot pain. He or she may refer you to a doctor or surgeon who specializes in foot disorders. Before your appointment, you may want to write a list of answers to the following questions. When did your symptoms begin? Did your symptoms begin gradually or suddenly? What type of footwear do you wear for work? Do you participate in sports? If so, what types in particular? What medications and supplements do you take regularly? Your doctor may ask some of the following questions. Is the pain worse in certain pairs of shoes? Does any type of activity ease the pain or worsen it? Are you having pain in any other part of your body?
Non Surgical Treatment
You may be able to treat this problem at home. Avoid wearing tight, pointy, or high-heeled shoes. Choose well-fitted shoes with plenty of room for your toes. Put ice or a cold pack on the area for 10 to 15 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your skin. Take anti-inflammatory medicines to reduce pain and swelling. These include ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) and naproxen (such as Aleve). Rest your feet when you can. Reduce activities that put pressure on the toes, such as racquet sports or running. Try massaging your foot to relax the muscles around the nerve. If these steps do not relieve your symptoms, your doctor may have you use special pads or devices that spread the toes to keep them from squeezing the nerve. In some cases, a doctor may give a steroid shot to reduce swelling and pain. If these treatments do not help, your doctor may suggest surgery.
Surgical Treatment
When medications or other treatments do not work, podiatric surgery may be required. The most common surgical procedure for treating Morton?s neuroma is a neurectomy, in which part of the nerve tissue is removed. Although this procedure effectively removes the original neuroma, sometimes scar tissue known as a stump neuroma forms at the site of the incision. This may result in tingling, numbness, or pain following surgery. Surgery is effective in relieving or reducing symptoms for Morton?s neuroma patients in about 75% to 85% of all cases. Occasionally, minimally invasive radio frequency ablation is also used to treat Morton's neuroma.
 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.Causes
Morton's neuroma seems to occur in response to irritation, pressure or injury to one of the nerves that lead to your toes. Factors that appear to contribute to Morton's neuroma include. High heels. Wearing high-heeled shoes or shoes that are tight or ill fitting can place extra pressure on your toes and the ball of your foot. Certain sports. Participating in high-impact athletic activities such as jogging or running may subject your feet to repetitive trauma. Sports that feature tight shoes, such as snow skiing or rock climbing, can put pressure on your toes. Foot deformities. People who have bunions, hammertoes, high arches or flatfeet are at higher risk of developing Morton's neuroma.
Symptoms
A Morton's neuroma causes a "burning" sharp pain and numbness on the bottom of the foot in the involved area, and this pain and numbness can radiate to the nearby toes. The pain is usually increased by walking or when the ball of the foot is squeezed together and decreased with massaging. It may force a person to stop walking or to limp from the pain.
Diagnosis
You might first seek advice from your family doctor about your foot pain. He or she may refer you to a doctor or surgeon who specializes in foot disorders. Before your appointment, you may want to write a list of answers to the following questions. When did your symptoms begin? Did your symptoms begin gradually or suddenly? What type of footwear do you wear for work? Do you participate in sports? If so, what types in particular? What medications and supplements do you take regularly? Your doctor may ask some of the following questions. Is the pain worse in certain pairs of shoes? Does any type of activity ease the pain or worsen it? Are you having pain in any other part of your body?
Non Surgical Treatment
You may be able to treat this problem at home. Avoid wearing tight, pointy, or high-heeled shoes. Choose well-fitted shoes with plenty of room for your toes. Put ice or a cold pack on the area for 10 to 15 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your skin. Take anti-inflammatory medicines to reduce pain and swelling. These include ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) and naproxen (such as Aleve). Rest your feet when you can. Reduce activities that put pressure on the toes, such as racquet sports or running. Try massaging your foot to relax the muscles around the nerve. If these steps do not relieve your symptoms, your doctor may have you use special pads or devices that spread the toes to keep them from squeezing the nerve. In some cases, a doctor may give a steroid shot to reduce swelling and pain. If these treatments do not help, your doctor may suggest surgery.

Surgical Treatment
When medications or other treatments do not work, podiatric surgery may be required. The most common surgical procedure for treating Morton?s neuroma is a neurectomy, in which part of the nerve tissue is removed. Although this procedure effectively removes the original neuroma, sometimes scar tissue known as a stump neuroma forms at the site of the incision. This may result in tingling, numbness, or pain following surgery. Surgery is effective in relieving or reducing symptoms for Morton?s neuroma patients in about 75% to 85% of all cases. Occasionally, minimally invasive radio frequency ablation is also used to treat Morton's neuroma.
